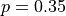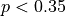Hypotheses#
Discussion Questions#
2007, Free Response, #5
Researchers want to determine whether drivers are significantly more distracted while driving when using a cell phone than when talking to a passenger in the car. In a study involving 48 people, 24 people were randomly assigned to drive in a driving simulator while using a cell phone. The remaining 24 were assigned to drive in the driving simulator while talking to a passenger in the simulator. Part of the driving simulation for both groups involved asking drivers to exit the freeway at a particular exit. In the study, 7 of the 24 cell phone users missed the exit, while 2 of the 24 talking to a passenger missed the exit.
Would this study be classified as an experiment or an observational study? Provide an explanation to support your answer.
State the null and alternative hypotheses of interest to the researchers.
One test of significance that you might consider using to answer the researchers’ question is a two-sample z-test. State the conditions required for this test to be appropriate. Then comment on whether each condition is met.
Using an advanced statistical method for small samples to test the hypotheses in part b, the researchers report a p-value of 0.0683. Interpret, in everyday language, what this p-value measures in the context of this study and state what conclusion should be made based on this p-value.
2008, Free Response Form B, #4
A researcher wants to conduct a study to test whether listening to soothing music for 20 minutes helps to reduce diastolic blood pressure in patients with high blood pressure, compared to simply sitting quietly in a noise-free environment for 20 minutes. One hundred patients with high blood pressure at a large medical clinic are available to participate in this study.
Propose a design for this study to compare these two treatments.
The null hypothesis for this study is that there is no difference in the mean reduction of diastolic blood pressure for the two treatments and the alternative hypothesis is that the mean reduction in diastolic blood pressure is greater for the music treatment. If the null hypothesis is rejected, the clinic will offer this music therapy as a free service to their patients with high blood pressure. Describe Type I and Type II errors and the consequences of each in the context of this study, and discuss which one you think is more serious.
2009, Free Response, #5
For many years, the medically accepted practice of giving aid to a person experiencing a heart attack was to have the person who placed the emergency call administer chest compression (CC) plus standard mouth-to-mouth resuscitation (MMR) to the heart attack patient until the emergency response team arrived. However, some researchers believed that CC alone would be a more effective approach.
In the 1990s a study was conducted in Seattle in which 518 cases were randomly assigned to treatments: 278 to CC plus standard MMR and 240 to CC alone. A total of 64 patients survived the heart attack: 29 in the group receiving CC plus standard MMR, and 35 in the group receiving CC alone. A test of significance was conducted on the following hypotheses.
: : The survival rates for the two treatments are equal.
: : The treatment that uses CC alone produces a higher survival rate.
This test resulted in a p-value of 0.0761.
Interpret what this p-value measures in the context of this study.
Based on this p-value and study design, what conclusion should be drawn in the context of this study? Use a significance level of α = 0.05.
Based on your conclusion in part b, which type of error, Type I or Type II, could have been made? What is one potential consequence of this error?
2012, Free Response, #5
A recent report stated that less than 35 percent of the adult residents in a certain city will be able to pass a physical fitness test. Consequently, the city’s Recreation Department is trying to convince the City Council to fund more physical fitness programs. The council is facing budget constraints and is skeptical of the report. The council will fund more physical fitness programs only if the Recreation Department can provide convincing evidence that the report is true. The Recreation Department plans to collect data from a sample of 185 adult residents in the city. A test of significance will be conducted at a significance level of a = 0.05 for the following hypotheses.
:
:
where p is the proportion of adult residents in the city who are able to pass the physical fitness test.
Describe what a Type II error would be in the context of the study, and also describe a consequence of making this type of error.
The Recreation Department recruits 185 adult residents who volunteer to take the physical fitness test. The test is passed by 77 of the 185 volunteers, resulting in a p-value of 0.97 for the hypotheses stated above. If it was reasonable to conduct a test of significance for the hypotheses stated above using the data collected from the 185 volunteers, what would the p-value of 0.97 lead you to conclude?
Describe the primary flaw in the study described in part b, and explain why it is a concern.
2018, Free Response, #6
TODO (GOOD ONE TO GO OVER IN GREAT DETAIL!)