Binomial Distribution#
Binomial Random Variable#
Definition#
Recall a Bernoulli Random Variable is defined over a sample space of binary outcomes, a success s that occurs with probability 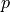 of success and a failure
of success and a failure f that occurs with probability 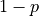 ,
,
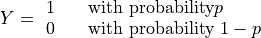
Consider a random variable defined as the sum of 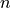 Bernoulli random variables,
Bernoulli random variables, 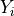
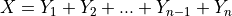
Where each 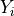 takes the value 1 with probability
takes the value 1 with probability 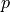 or it takes the value 0 with probabilitiy
or it takes the value 0 with probabilitiy 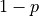
TODO
From Conditional Probability, the probability of an intersection of independent events is the product of individual probabilitiy,
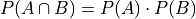
TODO
Conditions#
In order for an experiment to be Binomial, the experiment must the conditions just discussed. The summary below provides a list of each condition.
Parameters#
The Binomial Distribution has two parameters.
TODO
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
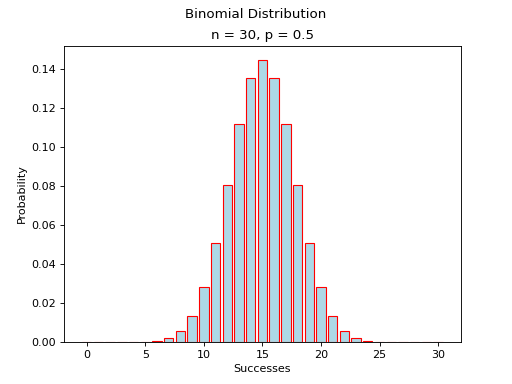
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
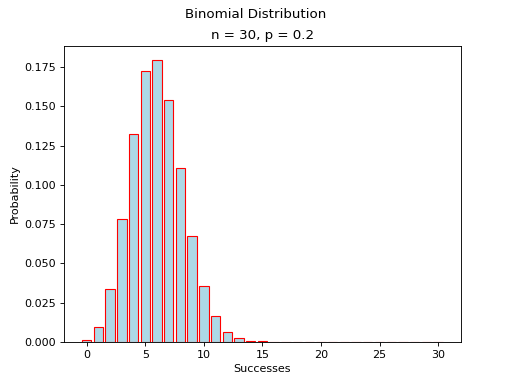
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
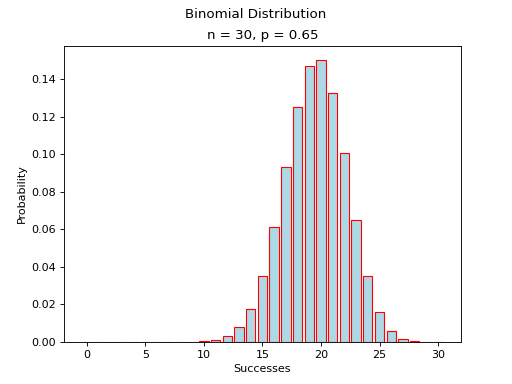
(Source code, png, hires.png, pdf)
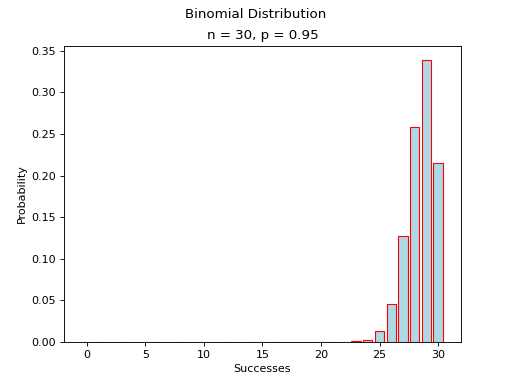
Probabilitiy Distribution#
TODO
Probability Density Function#
TODO
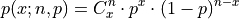
Cumulative Distribution Function#
TODO
By definition,
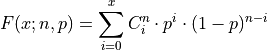
Expectation#
TODO
derive through rules of independent random variable sums
TODO
Standard Deviation#
TODO
TODO
TODO
derive through rules of independent random variable sums